How to Determine How Much Excess Reactant Is Left
Limiting Reactant Concept. 431 322 109 g of water.
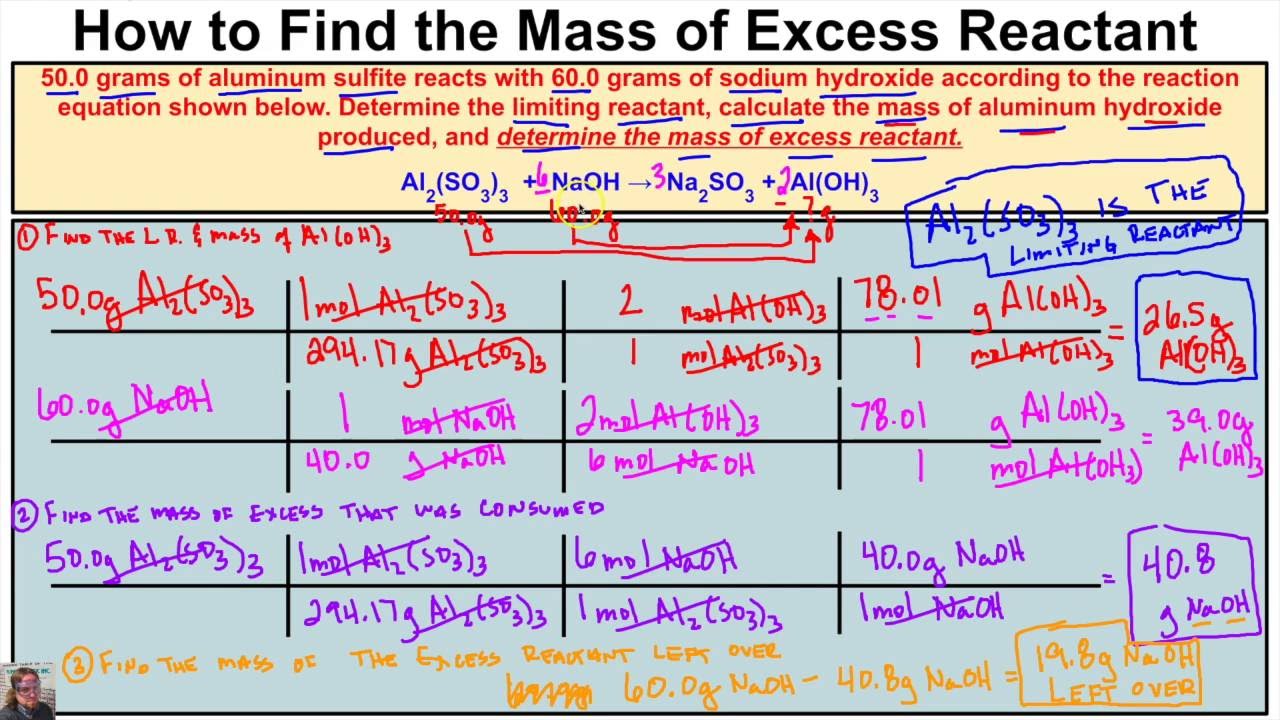
How To Calculate The Mass Of Excess Reactant Left Over In A Chemical Rea Chemistry Class Chemical Reactions Ap Chem
It also determines the amount of the final product that will be produced.

. The molar mass of iron can be found on the periodic table under the element symbol in the center. The reactant that produces the lesser of the two amounts will tell you the limiting reactant. Note that because so 2.
15 Limiting Reactant and Theoretical Yield - Cont. The ratio of limiting reagent or. At iitill tii lPClA system initially containing only PCl 5 at t ti f 0 100t a concentration of 0100 M has a Q c 0 which is less than 0030.
If the question had not stated excess carbon you would have to identify the limiting reactant prior to completing anything. How do we convert from the amount of reactant to amount of product. First find the ratios of the reactants then use the moles of each reactant and cross multiply to find how much of each reactant is required.
22 Percent Yields from Reactions Theoretical yield is calculated by assuming that the reaction goes to completion It is the maximum yield possible for the given reaction BUT in many reactions the reactants are not completely converted to. As we can see the limiting reagent or limiting reactant in a reaction is the reactant that gets completely exhausted and thus prevents the reaction from continuing forward. Note that we might have reasonably assumed that iron metal was the limiting reactant since it was present in lesser amount in grams initially 100 g of Fe and 150 g of Cl 2.
A Sandwich-Making Analogy This video from Noel Pauller uses the analogy of making sandwiches. Reactants to Products. Therefore limiting reagents often equals product.
A chemical equation is like a recipe for a reaction so it displays all the ingredients or terms of a chemical reaction. C we can calculate exactly how much additional reactant or product will form in order to reach equilibrium. To convert from grams to moles one must divide the given amount of grams by the molar mass of iron to convert to moles.
The limiting reactant or reagent can be determined by two methods. Calculate the amount of product using each reactant. The limiting reagents are the lesser in numbers and determine how much of a product will result.
The general problem Given the chemical equation and the masses of reactants determine the mass of. Often it is straightforward to determine which reactant will be the limiting reactant but sometimes it takes a few extra steps. Note that one product of the esterification reaction is water.
The determination of the limiting reactant is typically just a piece of a larger puzzle. The reactant that produces fewer moles of product is the limiting reagent because it limits the amount of product that can be produced. Skip to main content Search site.
After heating the mass of the anhydrous compound is found to be 322 g. H 2 O is the limiting reactant the Fe is the excess reactant and you will have 269 - 167 102 moles Fe left over. This is also an application of Le Chateliers principle.
More typically one reagent is completely used up and others are left in excess perhaps to react another day. C Cl 2 CCl 4. It is also wasteful.
The one that is less is the limiting reagent. A second method to drive the equilibrium towards product is to remove one of the products as it is formed. 7 125 g of copper are reacted with an excess of chlorine gas and 254 g of copperII chloride are obtained.
Calculate the theoretical yield and the. Chemists need a measurement that indicates how successful a reaction has been. The limiting reagent is that reactant that produces the least amount of.
1 Determine mass of water driven off. B How much of the excess reactant is left. To determine a limiting reagent follow all of the steps until you get to the ratio section.
Since lif is insoluble this is the final product. The limiting reagent is important because for higher effectivity you want a balanced reaction. 6 In the reaction of Zn with HCl 14015 g of ZnCl2 was actually formed although the theoretical yield was 143 g.
How many grams of excess reactant are left. In practice an excess of one reactant is used for two reasons. This measurement is called the percent yield.
This solution will use dimensional analysis also called the unit-factor or unit-label. The drawback in this method is that most of the excess reactant is left unreacted requiring extra steps to remove it. Of carbon with 1000 g of chlorine.
Once you have identified the limiting reactant you calculate how much of the other reactant it must have reacted with and subtract from the original amount. Determine the formula of the hydrate and then write out the name of the hydrate. In most limiting reactant stoichiometry problems the real goal is to determine how much product could be formed from a particular reactant mixture.
Calculate the molecular weight of each reactant and product. Na 2 CO 3--- 322 g 105988 gmol 00304 mol. What are the.
669 g P_4 P_4 is present in excess In a more clear form the reaction is P_4 s 6Cl_2 g rarr 4PCl_3 l Were asked to calculate how much of the excess reactant which we have to find remains after this reaction goes essentially to completion. BaO 2 s 2HClaq --- H 2 O 2 aq BaCl 2 aq Solution. To find the excess reactant we must first find the number of moles of each reactant present.
To determine how much product Fe 3 O 4 will be made multiply the limiting. Using the mole ration. 1 To drive the reaction to completion 2 To maximize the yield of products The reactant that is added in excess amount is called the excess reactant while the one in lower or limiting amount is called the limiting reactant or limiting reagent.
PCl 5 g PCl 3 g Cl 2 g K c 0030 Consider this equilibrium. 2 Determine moles of Na 2 CO 3 and water. Excess reagents are the chemical or chemicals left over the by-products of a reaction.
It includes the elements molecules or ions in the reactants and in the products as well as their states and the proportion for how much of each particle is create relative to one another through the stoichiometric coefficient. Search Search Go back to previous article. Finding the limiting reactant is an important step in finding the percentage yield of the reaction.
2 is the limiting reactant. But it turned out that Cl 2 was the limiting reactant. Iron metal is therefore in excess amount so there will be some Fe left over unreacted.
Perform this calculation for each reactant then compare the moles of product NO2 formed by the given amounts of O3 and NO to determine which reactant is the. The limiting reagent is that reactant that produces the least amount of. What was the percent yield.
Determine the mass of excess reagent left unreacted.

Introduction To Limiting Reactant And Excess Reactant Science Sciencewithtylerdewitt Tylerdewitt Tu Chemistry Help Apologia Chemistry High School Chemistry

Stoichiometry Limiting Excess Reactant Theoretical Percent Yield Chemistry Study Help Chemistry Videos Tutorial
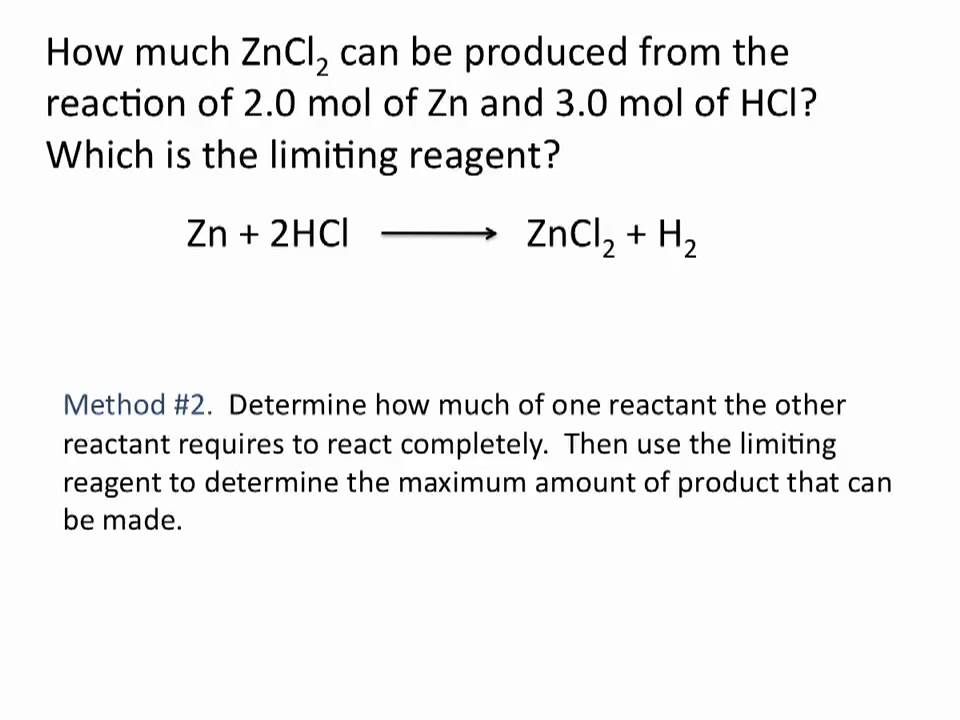
Limiting Reagent Chemistry Tutorial Youtube Chemistry Tutorial School

Theoretical Actual Percent Yield Error Limiting Reagent And Excess Reactant That Remains Youtube Ch 8 Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Notes Chemistry
Comments
Post a Comment